
1) Sleeve Gastrectomy
Sleeve gastrectomy surgery is especially used in patients who prefer to eat excessive amounts and high calorie meals. Sleeve gastrectomy is done in small closed pores ranging from 5 to 12 mm in size. During the operation of the sleeve gastrectomy, the stomach is reduced in size to about 10% of its previous size. The incised stomach is taken out without opening an additional hole. The left stomach is about 100-150 ml. A device is used that cuts the middleman and three-ply titanium punches on both sides of the incision line called the stapler on the staple. The crotch surface is sewn on the second layer seams and fibrin glue is sprayed on to prevent infiltration and bleeding. Leakage test is performed by giving painted water with methylene blue after air first during surgery. Routinely place a drain near the nipple. Sutures are placed in the surgical holes to prevent hernia formation.
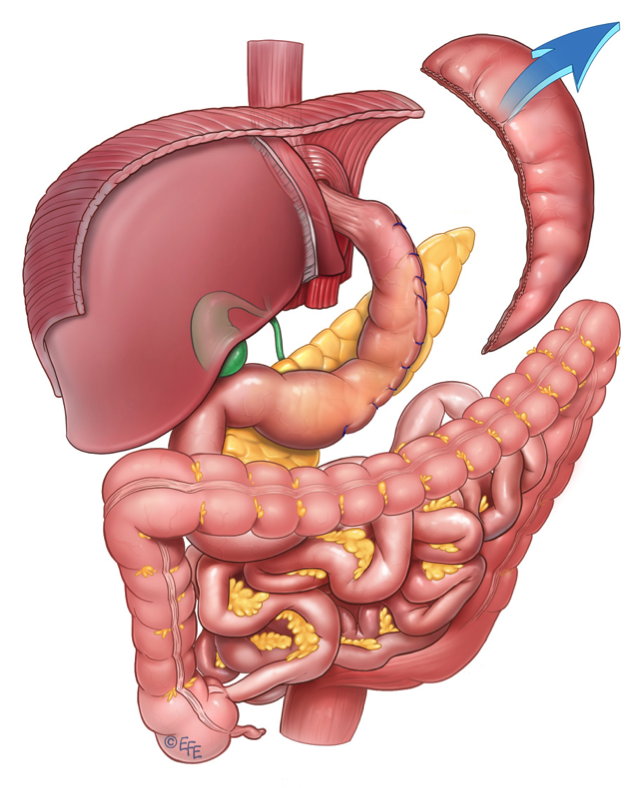
Sleeve gastrectomy surgery has 2 types of effects on obesity:
2) Gastric Bypass Surgery (Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass)
Gastric bypass surgery is preferred for patients with Type 2 diabetes who have a predominantly sweet food intolerance and metabolic problems. Gastric bypass surgery is also performed in small holes ranging in size from 5 to 12 mm as in other methods. During gastric bypass surgery, the size of the stomach is reduced to about 25-30 ml. Then a transition is made between the stomach and the small intestine. These operations are performed with devices called stapler (stapler). The crotch surfaces are trimmed with the second layer seams. In the second step, another transition is made between the intestine and the intestine. Postoperative air and methylene blue tests determine whether or not there is leakage. There is a resistance to the gastrointestinal tract. The surgical holes are closed.

Gastric Bypass Surgery has 3 types of effects:
3) Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD-DS)
BPD-DS surgery is performed with closed approach. This surgical technique is often not preferred as the first operation, it is used in patients who have undergone previous obesity surgery and whose results are inadequate. This surgical technique is the combination of both Sleeve Gastrectomy and Gastric Bypass Surgery. Unlike Gastric Bypass Surgery, absorption is much more reduced.

BPD-DS surgery has 3 types of effects on obesity:
4) Gastric Band (Gastric Cuff)
Gastric Band surgery is also performed with closed technique. The band is placed underneath the junction of esophagus and stomach. 15-30mL of stomach volume is preserved above the band. Hence, patient achieves satiety much quicker. The fact that the long term results are not very successful, the rate of conversion to other surgeries, and the necessity of being removed due to various complications, makes the gastric band less applicable.

Results of Obestiy and Metabolic Surgeries:
After Sleeve Gastrectomy, patients lose 70% of excessive weight on average. After Gastric Bypass Surgery, patients lose 80% of excessive weight on average. After BPD-DS, patients lose 90% of excessive weight on average. This rate is around 30% for Gastric Band Surgery.
The rates of improvement in the problems caused by obesity are as follows:
Complications and Side-Effects of Obesity and Metabolic Surgery:
The surgeries performed due to metabolic causes, such as obesity and type 2 diabetes, are safe. A thorough review and preparation before surgery will increase the safety of surgeries. Although rare, the main causes of these problems are as follows:
Complications:
Side Effects: